Author: Doctor Paolo Pirozzi
34-year-old patient, operated at the end of July for surgery for a right ankle prosthesis: the joint was affected by an early and severe form of arthrosis caused by a previous road accident that occurred 5 years earlier with consequent first fibular stabilization operation and tibial.

Test with Baiobit
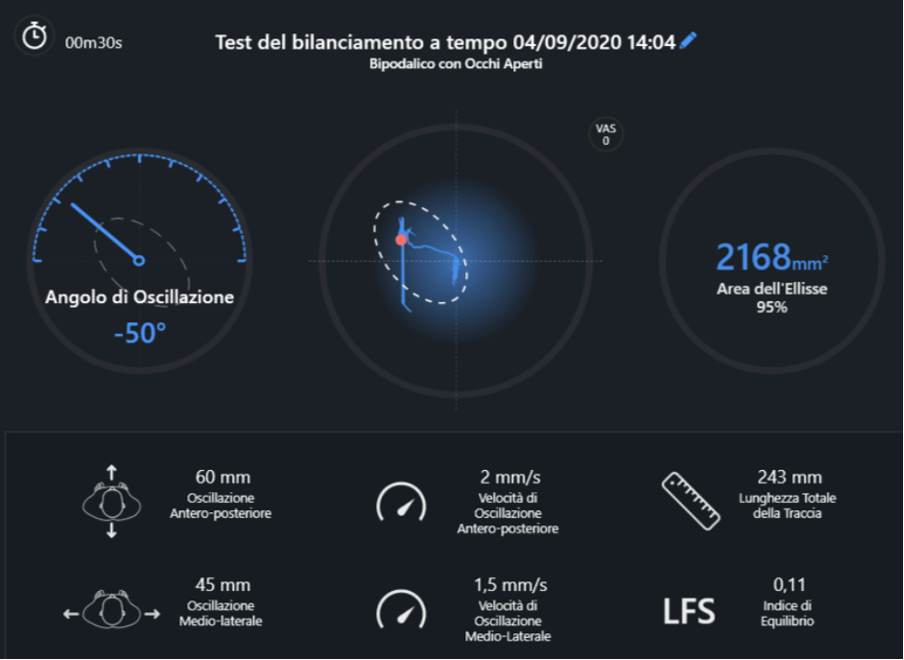
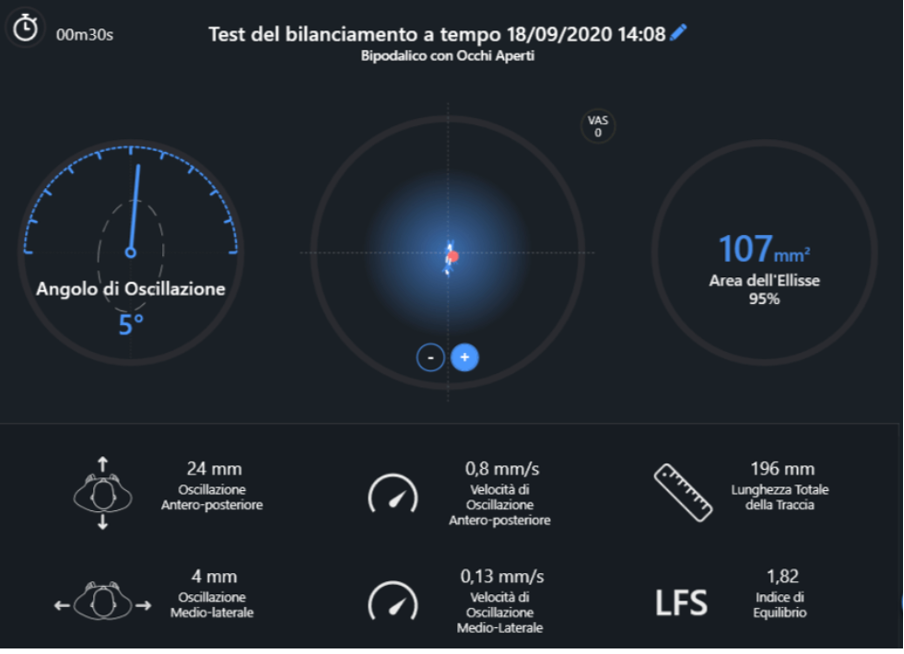
In agreement with the referring orthopedist, the rehabilitation intervention began a month and a half after the day of the operation to ensure good healing of the tissues and the wound: the primary objective was to restore the full load on both legs by removing the crutches. For this reason, we evaluated the static bipedal balance without supports on the first day of treatment (4/9/2020), the day on which the patient was still walking with a crutch, and after 2 weeks (18/9/2020), the day when the patient walked without any more supports.
Rehabilitation Program
The rehabilitation program, in the initial phase, was characterized by a progressive re-education path to bipedalism and monopodial load with support. Given the type of surgery, it is necessary to keep the particularity of the ankle operated to the maximum right away to avoid adhesions and consequent difficulties in daily life activities: for this reason, it is essential to ensure correct load distribution from the very first stages of rehabilitation.
Exercises with Baiobit
Bipodalic static balance exercises in biofeedback:
Bipodalic Balance with Eyes Open – Third Evaluation
Results
After 2 weeks of rehabilitation and 6 physiotherapy sessions carried out, thanks to the data acquired with the Baiobit sensor, it was possible to statistically and objectively quantify the improvement in the load distribution of the patient in bipedalism load. More specifically, it turned out that:
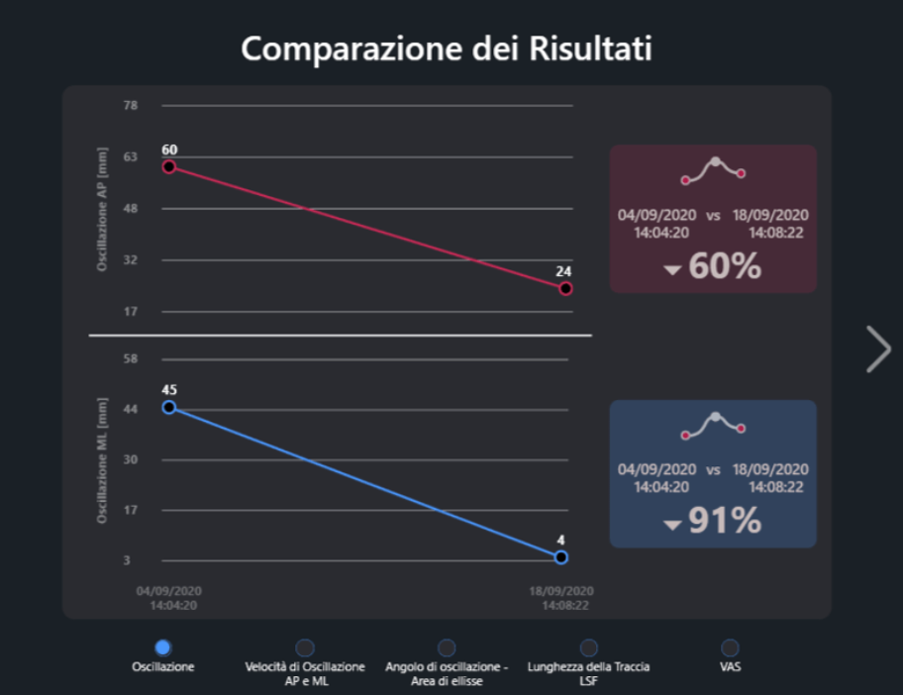
- The anteroposterior oscillation was reduced by 60%
- The mid-lateral oscillation was reduced by 91%
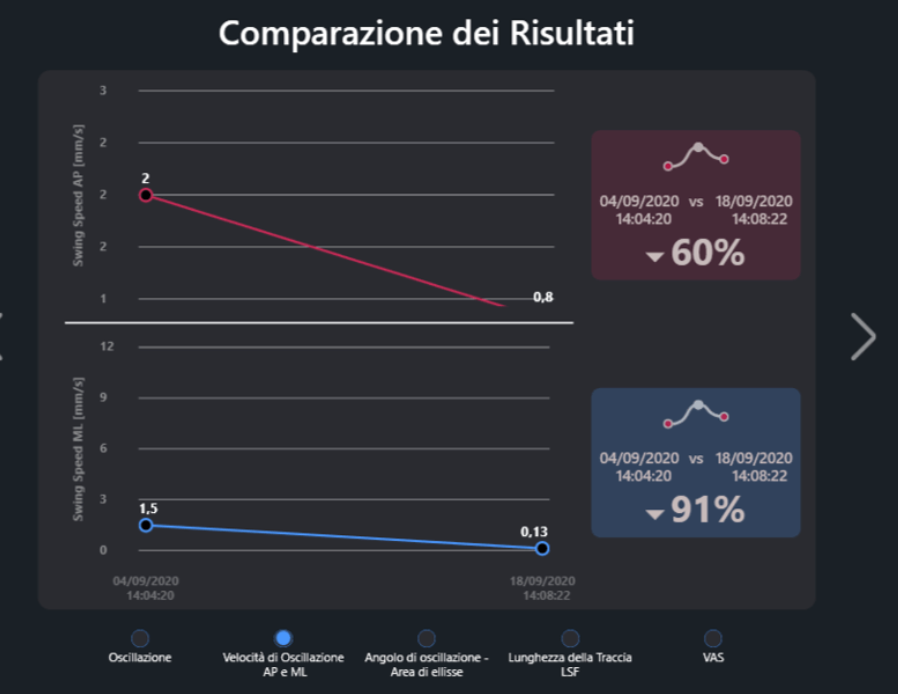
- Anterior-posterior rocking speed decreased by 60%
- Mid-lateral swing rate decreased by 91%
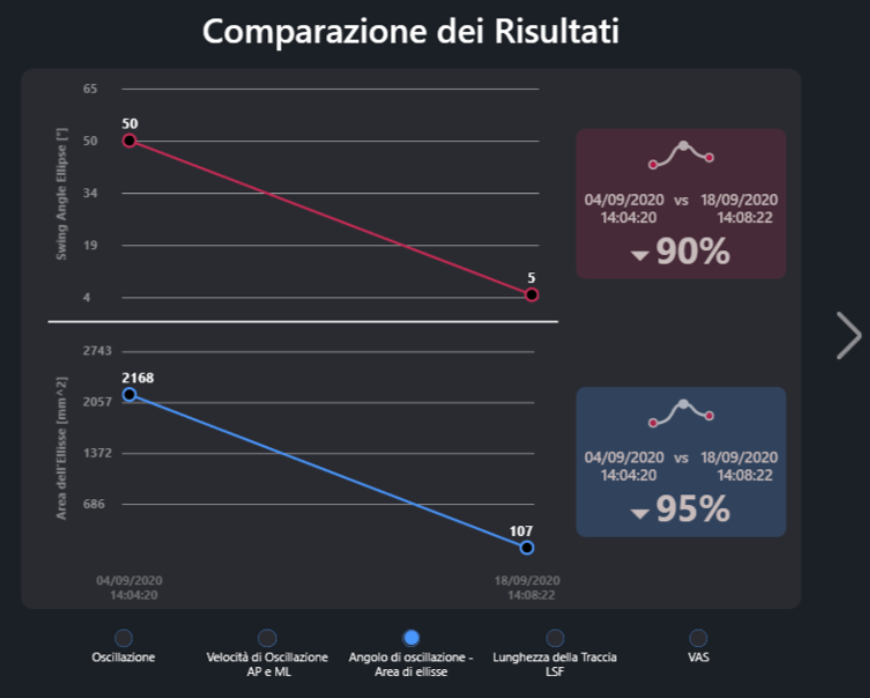
- The swing angle was reduced by 90%
- The area of the ellipse has been reduced by 95%
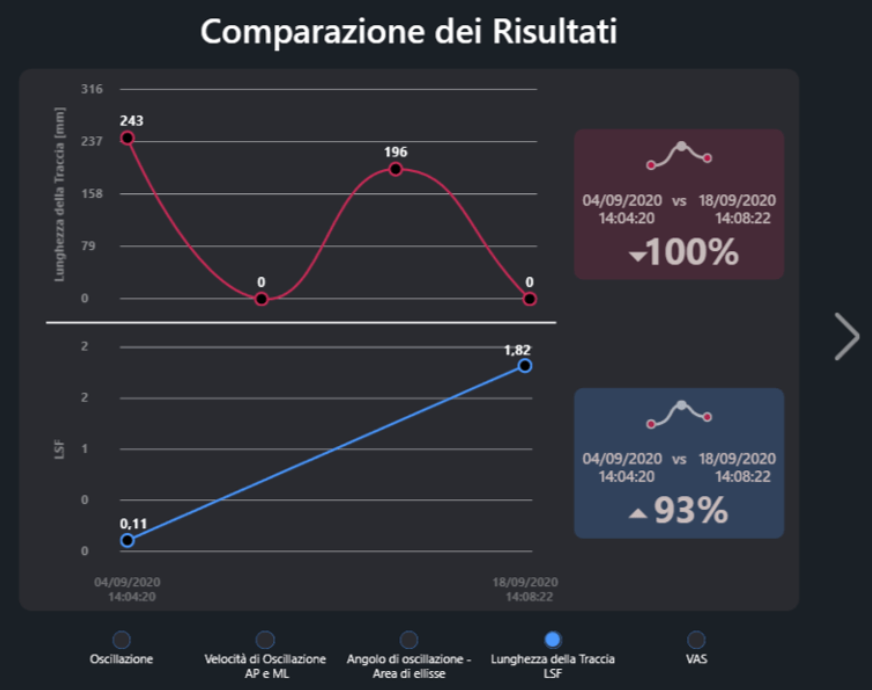
- Track length has been reduced by 100%
- The equilibrium index has improved by 93%
Comparison of Antero-Posterior and Medio-Lateral Oscillation:
Comparison of Antero-Posterior and Mid-Lateral Oscillation Speeds:
Comparison of Oscillation Angle and Ellipse Area:
Comparison of Track Width and Equilibrium Index: